Lub Pob Valve Floating yog dab tsi?
A lub pob valve ntabyog ib qho ntawm cov homlub pob valve, thiab qhov sib xws yogtrunnion mounted pob valve. Qhov nta ib lub pob tsis muaj kev txhawb nqa tuav tsuas yog ntawm ob lub rooj zaum kaw. Lub qia txuas nrog lub pob yooj ywm, cia nws "ntab." Nyob rau hauv qhov siab nruab nrab, lub pob txav mus rau lub rooj zaum hauv qab, tsim kom muaj kev sib khi nruj ntawm sab qhov hluav taws xob.
Cov Cheebtsam Tseem Ceeb
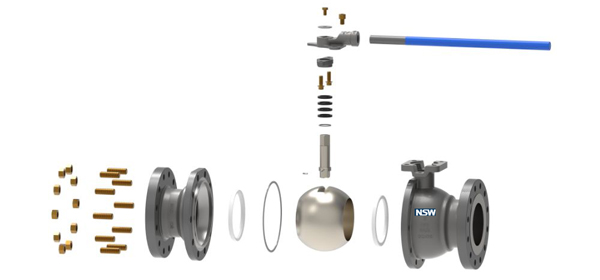
• Lub cev pob valve / lub hau npogTug: Cov khoom tseem ceeb ntawm lub valve
• Lub Pob ValveTug: Lub voos xwmfab uas txav tau dawb nrog lub qhov
• Lub qhov (valve stem): Xa lub zog mus rau lub pob
• Cov Rooj Zaum: Ob lub qhov sib khi ua ke
• Cov ntsaws ruaj ruajPTFE los yog cov khoom sib xyaw ua ke
Cov Lus Qhia Txog Kev Siv
| Cov Qauv | Ntau yam |
|---|---|
| Loj (DN) | 15 – 800 |
| Siab (PN) | 1.6MPa - 32.0MPa |
| Kev Sib Txuas | Xov (int/ext), Flanged, Welded, Wafer, Clamp |
| Kub | -196°C txog 550°C |
| Kev ua haujlwm | Phau Ntawv / Pneumatic / Hluav Taws Xob |
| Cov ntaub ntawv | Cast/Carbon/Forged Steel, Stainless |
| Cov Qauv | GB, DIN, API, ANSI |
Cov Qauv Tsim Kho ntawm Lub Pob Valve Uas Muaj Floating
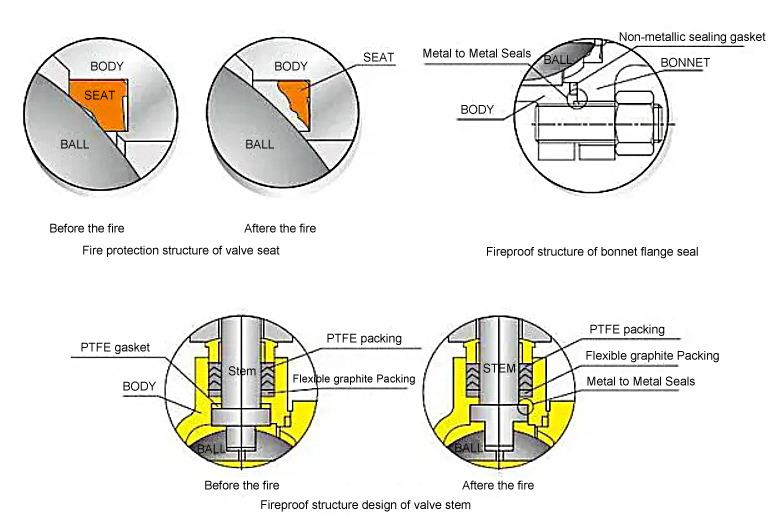
1. Tsim Lub Rooj Zaum Ob Chav-Sealing
Kev siv lub rooj zaum uas tsis muaj kev sib txhuam tsawg ua rau lub zog ua haujlwm tsawg dua thaum ua kom ntseeg tau tias tsis muaj kev xau los ntawm kev sib khi ob sab.
2. Qia tsis sib haum
Tus kav tiaj tiaj tiv thaiv kom tus kov tsis sib luag. Tus kov sib luag = Qhib; Tus kov ntsug = Kaw.
3. Qhov Xauv Kev Nyab Xeeb
Ob lub qhov xauv ntawm qhov qhib/kaw tag nrho tiv thaiv kev ua haujlwm tsis tau xav txog—qhov tseem ceeb rau cov kav dej txaus ntshai.
4. Lub qia tsis tawg
Ib lub xub pwg sib xyaw ua ke tiv thaiv cov qia tawm thaum muaj kev kub ntxhov ntau dhau, tswj kev ruaj khov ntawm lub foob.
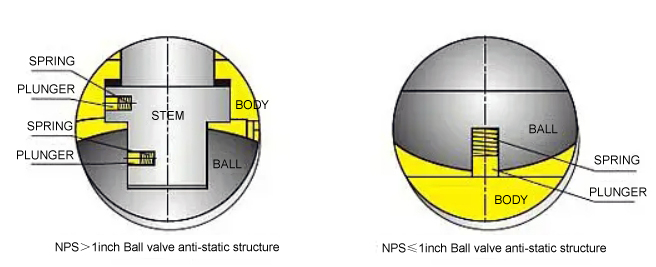
5. Lub Tshuab Tiv Thaiv Kev Ruaj Ntseg
Cov springs hauv av tso tawm cov hluav taws xob zoo li qub uas tsim los ntawm kev sib txhuam—qhov tseem ceeb rau cov khoom siv hluav taws xob uas yooj yim hlawv xws li LNG lossis propane.
6. Kev Tsim Kho Kom Muaj Kev Nyab Xeeb Hluav Taws
Cov foob pob hlau-rau-hlau sib txuas thaum muaj hluav taws:
• Kev sib cuag ntawm lub pob/lub cev hloov chaw lub rooj zaum uas raug hlawv
• Cov roj hmab hluav taws kub graphite nthuav dav kom thaiv cov dej xau
•API 607/ua raws li 6FA
7. Lub Cev Sib Koom Tes Tsis Muaj Qhov Tawg
Kev tsim qauv flange interlocking tshem tawm qhov kev vam khom gasket, tiv thaiv kev xau sab nraud hauv qab qhov xwm txheej hnyav.
Cov Ntawv Thov Kev Lag Luam
• Kev Pabcuam Dav Dav: Dej, cov kuab tshuaj, cov kua qaub
• Cov Khoom Tseem Ceeb: Oxygen, H₂O₂, methane
• Ib puag ncig hnyav:
Cov chaw tsim tshuaj petrochemical
Cov kav dej roj av (tiv taus H₂S)
Cov txheej txheem cryogenic
Kev thauj cov slurry uas muaj corrosion ntau
Cov txiaj ntsig ntawm cov pob valve uas ntab thiab cov kev txwv
Zoo:
✓ Tsim qauv me me thiab yooj yim rau kev saib xyuas
✓ Kev kaw ruaj khov
✓ Tsis tshua muaj dej ntws
✓ Ua haujlwm sai 90°
Qhov Tsis Zoo:
✘ Kev sib txhuam ntawm lub rooj zaum txwv tsis pub siv high-P/T
✘ Tsis yog rau cov slurries (kev pheej hmoo ntawm qhov groove clogging)
✘ Yuav tsum tau kev teeb tsa uas muaj kev txawj ntse
Cov Txheej Txheem Kev Teeb tsa & Kev Txij Nkawm
Cov Kev Cai Rau Kev Txhim Kho
• Teeb tsa kab rov tav rau ntawm cov chaw tiaj tiaj
• Tsis txhob muaj kev cuam tshuam ntawm cov dej ntws ze ntawm lub pob
• Xyuas kom tsis muaj kev cuam tshuam rau kev nkag mus
Daim Ntawv Teev Xyuas Kev Txij Nkawm
• Txhua Peb Hlis: Tshawb xyuas seb lub pob/cov nplhaib khawb puas muaj kev puas tsuaj
• Txhua xyoo:
Siv lubricating cov bearings
Xyuas kom meej cov nqi torque
Kuaj cov ntsaws ruaj ruaj thaum muaj xwm ceev
• Tom qab kaw: Ntxuav qhov chaw kom tsis txhob muaj cov khoom seem uas ua rau cov khoom seem tawg
Floating vs.Trunnion Mounted Pob ValvesKev Sib Piv Txog Kev Siv Tshuab
| Aspect | Hom ntab | Trunnion Mounted Hom |
|---|---|---|
| Txoj Cai Sealing | Lub zog ntawm xov xwm thawb lub pob mus rau lub rooj zaum | Cov springs yuam cov rooj zaum mus rau lub pob |
| Kev Teeb Tsa | Ib lub qia sab saud | Dual trunnion-txhawb nqa |
| Kev Ntsuas Siab | ≤Chav Kawm 1500 (DN300 siab tshaj) | Txog li Chav Kawm 2500 (DN1500+) |
| Cov ntawv thov | Cov tshuab siab qis-nruab nrab | Cov kav dej loj (piv txwv li West-East Gas Project) |
Cov Lus Qhia Txog Kev Xaiv
Xaiv cov twj tso kua dej uas ntab rau cov kev daws teeb meem pheej yig thiab me me hauv qab Chav Kawm 600. Xaiv cov twj tso kua dej uas tau teeb tsa los ntawm trunnion thaum tuav:
• Kev Nyuaj Siab > Chav Kawm 900
• Kev caij tsheb kauj vab ntau zaus
• Cov khoom siv uas ua rau kub hnyiab los yog tawg
Lub sijhawm tshaj tawm: Lub Kaum Ob Hlis-10-2024